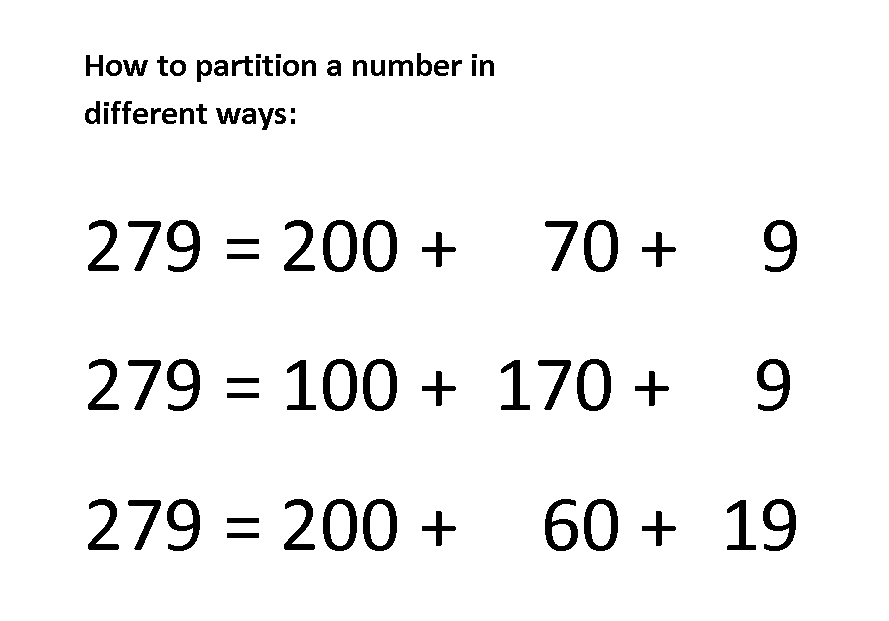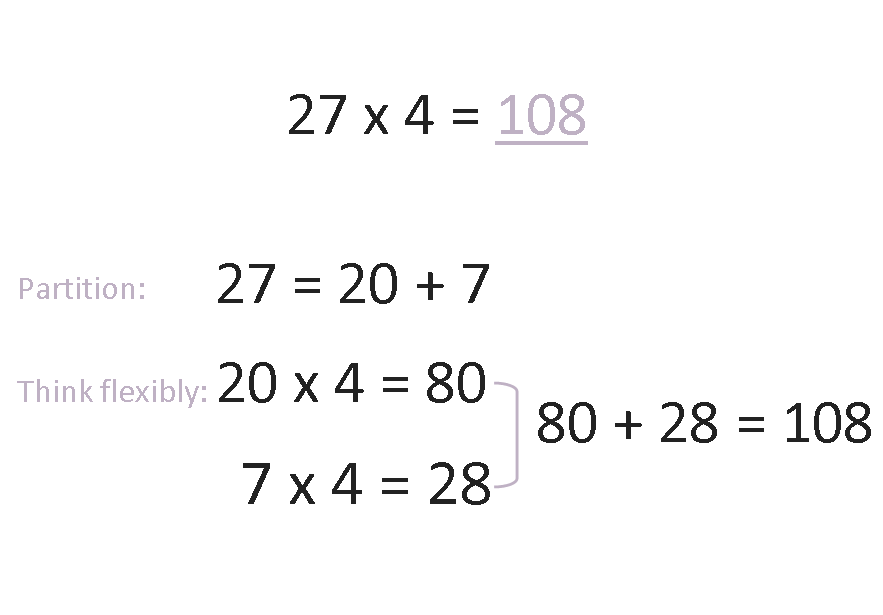5 Must Know Maths Terms
Maths in the classroom has changed quite a lot over the years. With a more practical approach to teaching maths, children are engaging with innovative resources in the classroom. These new resources and approaches work wonders in the classroom and in tutoring sessions, so why not see how these can benefit homework time as well. Get up to speed with how maths in lower primary school is being taught and what strategies you need to know.
1. What is ‘partitioning’?
Partitioning is splitting a number into component parts.
Why are children taught partitioning?
Helps with grasping place value concepts (understanding the value of each digit)
Allows children to work flexibly with numbers, which helps with problem solving and mental calculations
How partitioning helps with mentally calculating addition problems
How partitioning helps with mentally calculating multiplication problems
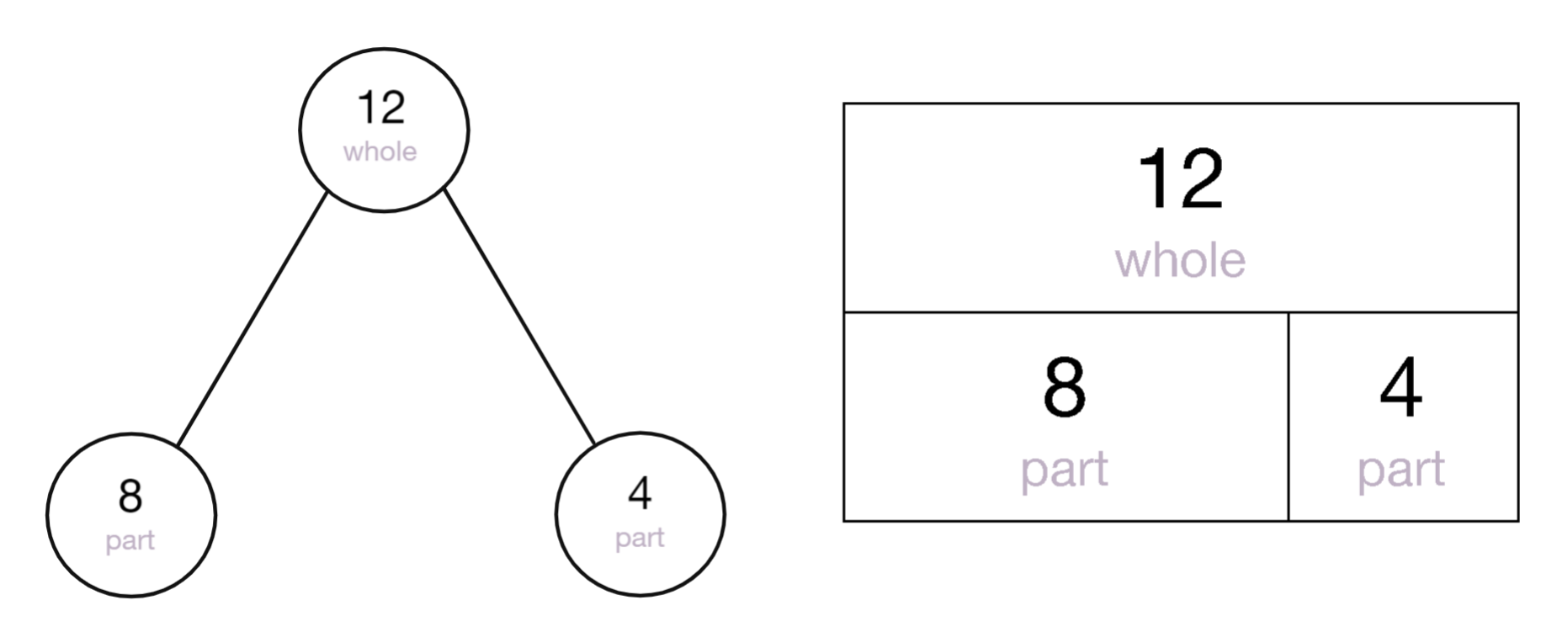
2. What is the ‘part-whole model’ (or part-part-whole model)?
Part-whole models are based on the concept of how numbers can be split into parts. These models show the relationship between the whole numbers and the component parts.
Why are part-whole models used?
Helps with interpreting, visualising and solving word problems
Clearly shows the inverse of addition and subtraction, as well as multiplication and division
Reinforces the concept of component parts - check that you are using the correct language!
Visually represent problems, supporting the concrete - pictorial - abstract approach
Using a part-whole bar model can help with
finding the missing number element.
3. What is ‘subitising’?
This term describes being able to look at a small number of objects and instantaneously recognising how many there are, without counting them.
Why is this skill important?
Helps link the word and symbol to a digit
Builds mental images of numbers, which also supports learning number facts
Helps relate numbers to actual groups of objects or items
Recognising the number of dots on a die without counting them is an example of subitising.
4. What are Base Ten blocks
(or Dienes blocks)?
These blocks are used to represent numbers physically. They can be manipulated to represent the place value of numbers. They’re often placed on a blank place value chart to reinforce the concept of place value.
Why are they used?
Children can physically manipulate the blocks to exchange them
Develops understanding of maths concepts (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division)
Using concrete materials helps understand the concept, rather than blindly follow a process
5. What is Numicon?
These manipulatives are a set of flat, plastic shapes with holes. Each piece represents a number from 1 to 10, and has its own colour.
Why is Numicon useful?
Can be physically manipulated to explore number
Based on the concrete-pictorial-abstract relationship, which links to the maths mastery approach
Useful for teaching many maths concepts (such as ordering numbers, counting, number bonds)
How Numicon can be used to find number bonds to 10.
Conclusion
Now you’re up to speed on the resources and strategies commonly being used with children in the classroom. You can see the value of using hands on materials, helping children to make concrete-pictorial-abstract connections. I use these strategies and tools when teaching in the classroom and during tutoring sessions.